Here are 200 SEO (Search Engine Optimization) terminology and terms related to SEO:
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) : SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is a digital marketing strategy aimed at improving a website’s visibility in search engine results. It involves optimizing various elements such as content, keywords, and technical aspects to enhance organic (non-paid) search rankings. The goal is to increase website traffic and attract relevant visitors.
🚀 Meta Tags 🚀 Sitemap.xml 🚀Robots.txt 🚀 Title tag 🚀 Header Tag 🚀 Canonicals Issue 🚀 Content Optimization 🚀 Layout 🚀 Website Speed
SERP (Search Engine Results Page) : SERP (Search Engine Results Page) refers to the web page displayed by a search engine in response to a user’s query. It lists relevant websites, links, and snippets that match the search query. SERPs may include paid advertisements, organic search results, featured snippets, and other elements to provide users with information.

Keywords : Keywords are specific words or phrases that users enter into search engines when looking for information online. In SEO and digital marketing, keywords are strategically chosen and optimized to improve a website’s visibility in search engine results. They play a crucial role in attracting relevant traffic to a website.

Long-tail keywords : Long-tail keywords are longer and more specific keyword phrases typically consisting of three or more words. They are used in SEO to target niche and highly specific search queries. Long-tail keywords often have lower search volume but higher conversion potential, as they cater to users with more specific search intents.
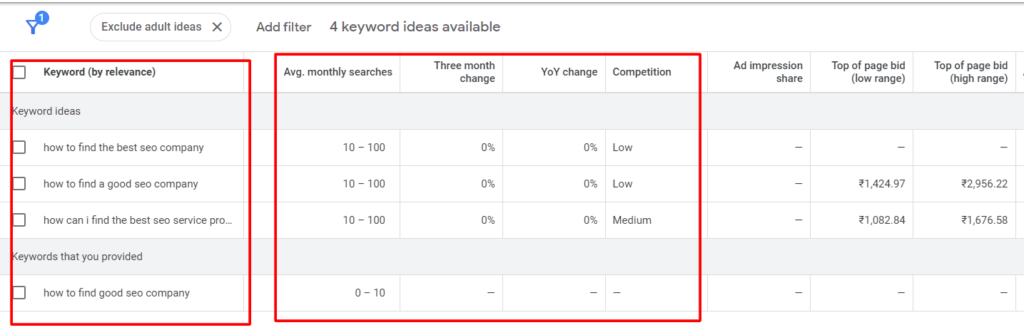
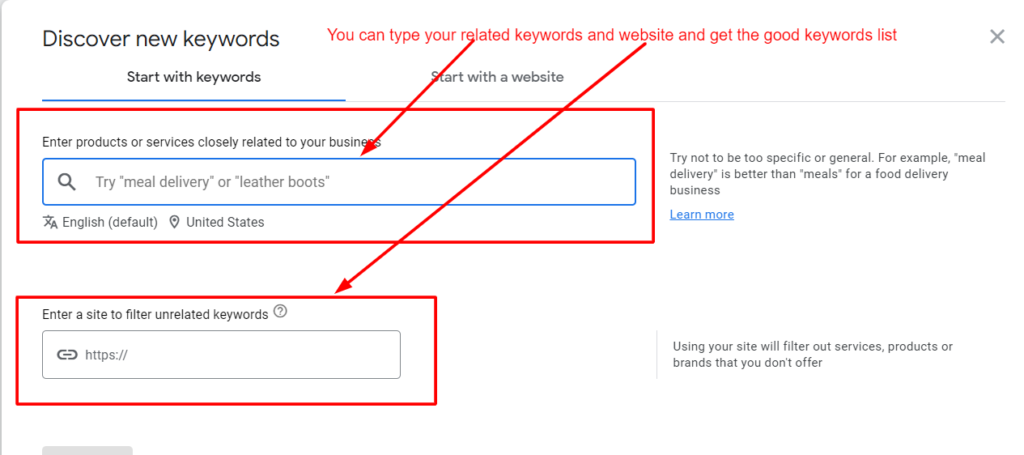
Keyword research : Keyword research is the process of identifying and analyzing specific words or phrases that users frequently enter into search engines. It’s a fundamental component of SEO and content strategy, aimed at finding relevant keywords to optimize web content for improved search engine rankings and attracting targeted organic traffic.
On-page SEO : On-page SEO, also known as on-site SEO, refers to the optimization of individual web pages to improve their search engine rankings and attract organic traffic. This involves optimizing elements such as content, meta tags, headings, images, and URLs to align with specific target keywords and provide a better user experience.

Off-page SEO : Off-page SEO involves optimizing factors outside of your website to improve its search engine ranking and online visibility. This includes activities like building high-quality backlinks from other websites, social media engagement, online reputation management, and content marketing on external platforms to establish authority, credibility, and trustworthiness in the eyes of search engines.

Organic search : Organic search refers to the natural and unpaid process of users finding and accessing a website through search engine results. It excludes paid advertising and involves users entering search queries into search engines like Google, Bing, or Yahoo, with the search engine returning relevant web pages based on algorithms and relevance.

Paid search : Paid search, also known as pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, involves marketers paying search engines to display their ads at the top or within search engine results pages. Advertisers bid on specific keywords, and they are charged a fee when users click on their ads. Paid search is a form of online advertising used to drive traffic and conversions.
SEM (Search Engine Marketing) : SEM (Search Engine Marketing) is a digital marketing strategy that involves promoting websites through paid advertising in search engine results pages (SERPs). It includes pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, where advertisers bid on keywords to display their ads, and other paid search methods to increase visibility, drive traffic, and achieve marketing goals.
PPC (Pay-Per-Click) : PPC (Pay-Per-Click) is an online advertising model where advertisers pay a fee each time their ad is clicked by a user. It’s commonly used in search engine marketing (SEM) and allows businesses to bid on keywords to have their ads displayed in search engine results, driving targeted traffic to their websites.
CTR (Click-Through Rate) : CTR (Click-Through Rate) is a digital marketing metric that measures the effectiveness of an online ad or link. It calculates the percentage of users who click on a specific ad or link after viewing it. CTR is often used to evaluate the performance and relevance of digital marketing campaigns.
Impressions : Impressions in digital marketing refer to the number of times an ad, web page, or piece of content is displayed or viewed by users, regardless of whether they take any action. It is a metric used to measure the visibility and reach of online assets, such as ads in a display campaign or search engine results.
Conversion rate : The conversion rate is a digital marketing metric that measures the percentage of website visitors or users who take a desired action, such as making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or filling out a contact form. It is a crucial metric for assessing the effectiveness of online marketing campaigns and website optimization efforts.
Landing page : A landing page is a standalone web page designed with a specific purpose, such as capturing user information or promoting a product or service. It is typically linked to from advertisements, emails, or search engine results and is optimized to encourage visitors to take a particular action, such as filling out a form or making a purchase.
Bounce rate : Bounce rate is a web analytics metric that measures the percentage of visitors who navigate away from a website or landing page after viewing only one page. It indicates the lack of engagement or relevance for visitors, often used to assess the quality of web content or user experience on a website.
SEO audit : An SEO audit is a comprehensive assessment of a website’s search engine optimization health. It involves analyzing various aspects such as on-page and off-page factors, technical SEO elements, content quality, and backlinks to identify issues, opportunities, and strategies for improving search engine rankings, organic traffic, and overall website performance.
Meta tags : Meta tags are HTML elements that provide information about a web page’s content to search engines and website visitors. Common meta tags include the meta title and meta description, which summarize a page’s topic and content. These tags help search engines understand and index web pages and can influence click-through rates in search results.
Title tag : A title tag is an HTML element that specifies the title of a web page. It appears in the browser’s title bar or tab and is crucial for search engine optimization. Title tags provide a concise description of the page’s content and help search engines understand its topic and relevance, influencing search rankings and user click-through rates.
Meta description : A meta description is an HTML element that provides a brief summary or description of the content on a web page. It appears in search engine results below the title tag and serves to inform users about the page’s content. A well-crafted meta description can influence click-through rates by enticing users to visit the page.
Header tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) : Header tags, such as H1, H2, H3, etc., are HTML elements used to structure and format content on web pages. H1 typically represents the main heading or title of the page, while H2, H3, and so on are used for subheadings. These tags help organize content hierarchically and improve both user experience and search engine optimization by providing clarity and structure to the page’s content.
Alt text (Alternative text) : Alt text, short for alternative text, is a descriptive attribute added to an HTML image tag. It provides a text description of an image’s content, allowing screen readers to convey the image’s meaning to visually impaired users. Alt text is also used by search engines for indexing images and can enhance accessibility and SEO.
Canonical URL : A canonical URL is a preferred version of a web page URL when multiple versions of the same content exist. It’s specified in the HTML code to indicate which page should be considered the original or primary source. This helps search engines avoid indexing duplicate content and consolidates ranking signals for the specified URL.
XML sitemap : An XML sitemap is a structured file that lists all the URLs on a website, helping search engines like Google crawl and index the site more efficiently. It provides essential metadata about each page, including how often it’s updated, when it was last modified, and its priority, improving search engine optimization and visibility.
Robots.txt : Robots.txt is a text file placed in a website’s root directory to instruct web crawlers which pages or sections should not be crawled or indexed. It’s used for controlling search engine access to specific content, such as private or duplicate pages, and can influence a website’s search engine optimization and visibility.
Crawling : Crawling, in the context of search engines, refers to the automated process by which search engine bots or spiders systematically browse the internet, visiting web pages and indexing their content. It’s a fundamental step in the search engine indexing process, allowing search engines to catalog and rank web pages for search results.
Indexing : Indexing is the process by which search engines, like Google, catalog and store web pages in their databases. During indexing, search engine bots analyze the content, structure, and metadata of web pages. This information is then used to rank and display relevant web pages in response to user search queries.
Crawl budget : Crawl budget is the allocated amount of time and resources search engines dedicate to crawling and indexing a website’s pages. It is influenced by factors such as a website’s size, authority, and server performance. Optimizing crawl budget ensures that search engines prioritize indexing important pages, enhancing a site’s visibility in search results.
Page speed : Page speed refers to the time it takes for a web page to fully load and display its content to a user’s browser. It is a critical factor for user experience and SEO, as faster-loading pages provide better user satisfaction and tend to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Mobile optimization : Mobile optimization involves designing and configuring a website to provide an excellent user experience on mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. It includes responsive web design, fast loading times, mobile-friendly navigation, and content formatting that adapts to smaller screens. Mobile optimization is crucial for SEO and user engagement in a mobile-driven digital landscape.
Responsive design : Responsive design is a web design approach that ensures a website’s layout and content adapt dynamically to various screen sizes and devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and desktop computers. It provides an optimal user experience by resizing and rearranging elements to fit the screen, eliminating the need for separate mobile and desktop versions of a site.
Mobile-first indexing : Mobile-first indexing is a practice by search engines where they primarily use the mobile version of a website’s content to determine its search engine rankings and indexing, considering the mobile-friendliness of a site as a ranking factor. This shift reflects the growing importance of mobile browsing and user experience in search results.
User experience (UX) : User experience (UX) refers to the overall impression and satisfaction a user has when interacting with a product, service, or website. It encompasses elements like ease of use, accessibility, design, functionality, and performance. A positive UX enhances user satisfaction and loyalty, while a poor one can lead to frustration and abandonment.
Dwell time : Dwell time is a metric that measures the amount of time a website visitor spends on a particular web page before returning to the search results or navigating to another site. It is often used as an indicator of content engagement and relevance, with longer dwell times generally considered favorable for SEO.
User intent : User intent, in the context of search engine optimization (SEO), refers to the specific goal or purpose behind a user’s online search query. It reflects what the user is seeking, whether it’s information, products, services, or answers, and guides content and keyword optimization strategies to provide relevant results that align with that intent.
Voice search : Voice search is a technology that enables users to perform internet searches, access information, and interact with digital devices using spoken language commands and queries. It utilizes voice recognition and natural language processing to understand and respond to user requests, offering a hands-free and convenient way to access information and services.
Featured snippet : A featured snippet is a distinct search result displayed at the top of some Google search engine results pages (SERPs). It provides a concise and direct answer to a user’s query, often in the form of a snippet from a web page. Featured snippets aim to quickly address user questions, making them prominent in search results.
Rich snippets : Rich snippets are search results that are enhanced with additional information, making them more informative and visually appealing. These snippets typically include extra data like star ratings, reviews, pricing, and other structured data, providing users with a better understanding of a web page’s content before they click on the link. Rich snippets can improve click-through rates and user engagement in search results. They’re a way for search engines to present more context about a page’s content.
Schema markup : Schema markup is a structured data vocabulary added to the HTML code of web pages. It provides search engines with specific information about the content on a webpage. This structured data helps search engines understand the context and attributes of the content, which can lead to the creation of rich snippets and enhanced search results, improving the visibility and relevance of web pages in search engine results pages (SERPs). Schema markup is used to mark up various types of content, such as products, events, reviews, recipes, and more, making it easier for search engines to deliver precise and informative search results to users.
Google My Business (GMB) : Google My Business (GMB) is a free online platform and tool provided by Google that allows businesses to manage and optimize their online presence across various Google services, including Google Search and Google Maps. With GMB, businesses can create and maintain their business listings, provide key information like address, phone number, hours of operation, and respond to customer reviews. It helps local businesses improve their visibility in local search results, connect with potential customers, and showcase important details that can influence user decisions when searching for products or services in their area. GMB is a valuable tool for local SEO and online reputation management.
Local SEO : Local SEO, or Local Search Engine Optimization, is a digital marketing strategy focused on optimizing a business’s online presence to appear prominently in local search results. It aims to increase a business’s visibility to local customers when they search for products or services nearby.
NAP (Name, Address, Phone Number) :NAP, which stands for Name, Address, Phone Number, is a critical component of local SEO. It refers to the consistent and accurate listing of a business’s name, physical address, and contact number across online directories, websites, and search engine platforms. Maintaining NAP consistency helps improve local search rankings and ensures customers can easily find and contact the business.
Citation : A citation in the context of local SEO is an online reference to a business’s NAP (Name, Address, Phone Number) information. These references can appear on various websites, directories, and platforms. Citations play a crucial role in local search rankings, and consistent and accurate citations help establish a business’s credibility and visibility in local search results.
Backlinks : Backlinks, also known as inbound links or incoming links, are hyperlinks on external websites that point to a specific webpage on another website. They serve as a crucial factor in search engine ranking algorithms, indicating the credibility and authority of a website. Quality backlinks from reputable sources can improve a site’s SEO and visibility.
Link building : Link building is the strategic process of acquiring and creating high-quality backlinks to a website from external sources such as other websites, blogs, or online directories. It’s a fundamental component of off-page SEO, aimed at improving a website’s authority, trustworthiness, and search engine rankings by generating relevant and valuable links.
Anchor text : Anchor text is the clickable, visible text within a hyperlink. It provides context and informs users and search engines about the content of the linked page. Effective anchor text is descriptive, relevant, and optimized for SEO, helping search engines understand the topic and relevance of the linked content.
Link juice : Link juice is a colloquial term used in SEO to describe the value or equity passed from one webpage to another through hyperlinks. When a webpage links to another, it can transfer some of its authority, trustworthiness, and ranking power, influencing the linked page’s search engine rankings. High-quality backlinks are often associated with significant link juice.
NoFollow link : A NoFollow link is a hyperlink on a webpage that includes the rel=”nofollow” attribute in its HTML code. It tells search engines not to pass authority, trust, or ranking value to the linked page. NoFollow links are often used for paid or untrusted links to prevent them from influencing search engine rankings.
DoFollow link : A DoFollow link is a standard hyperlink on a webpage that does not contain the rel=”nofollow” attribute in its HTML code. It allows search engines to follow the link and pass authority, trust, and ranking value from the source page to the linked page, potentially influencing the linked page’s search engine rankings.
Internal linking : Internal linking is the practice of creating hyperlinks within a website’s content that connect to other pages or resources within the same website. It helps users navigate the site, improves user experience, and distributes PageRank and authority throughout the website, potentially benefiting SEO and search engine rankings.
External linking : External linking, also known as outbound linking, is the process of creating hyperlinks on a webpage that point to other websites or resources outside of the website’s domain. These links provide additional information, sources, or references to users and can contribute to a well-rounded and informative content experience.
Domain authority (DA) : Domain Authority (DA) is a metric developed by Moz that quantifies the overall trustworthiness and authority of a website. It is measured on a scale from 0 to 100, with higher scores indicating a stronger online presence. DA considers various factors like backlinks, content quality, and site structure to assess a website’s ranking potential.
Page authority (PA) : Page Authority (PA) is a metric developed by Moz that assesses the relative strength and authority of a specific webpage within a website. It is measured on a scale from 0 to 100 and is influenced by factors such as backlinks, content quality, and on-page optimization. A higher PA indicates greater potential for the page to rank well in search engine results.
Trust flow : Trust Flow is a metric developed by Majestic that evaluates the quality and trustworthiness of a website’s backlink profile. It measures the trustworthiness of backlinks based on the credibility of linking domains. Higher Trust Flow scores indicate a more reliable and authoritative backlink profile, which can positively impact a website’s search engine rankings.
Citation flow : Citation Flow is a metric developed by Majestic that quantifies the quantity and volume of backlinks pointing to a website. It measures the link equity and influence of a website’s backlinks. While it assesses the quantity of links, it doesn’t consider the quality or trustworthiness of those links, making it essential to use in conjunction with other metrics for a comprehensive evaluation of a website’s backlink profile.
Google PageRank : Google PageRank was an algorithm developed by Google founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin to assess the importance of web pages based on the number and quality of links pointing to them. While it was once a key factor in Google’s ranking algorithm, it has been deprecated in favor of more complex algorithms like PageRank Sculpting and is no longer publicly visible.
EAT (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) : EAT, or Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness, is a set of criteria used by Google to assess the quality and credibility of web content. It plays a crucial role in evaluating pages, especially in areas like health, finance, and news. Websites and content creators are expected to demonstrate expertise, authority, and trustworthiness in their respective fields to rank well in search results. This concept helps ensure that users receive accurate and reliable information from reputable sources.
Content optimization : Content optimization is the process of enhancing the quality, relevance, and performance of online content to improve its visibility in search engine results. This involves keyword research, improving readability, optimizing meta tags, and enhancing user experience. The goal is to provide valuable content that aligns with user intent and SEO best practices.
Duplicate content : Duplicate content refers to identical or substantially similar content that appears on multiple web pages within the same website or across different websites. It can lead to confusion for search engines and users, potentially resulting in lower search rankings. Avoiding duplicate content is crucial for SEO to ensure content uniqueness and quality.
Thin content : Thin content refers to web pages or articles that lack substance, depth, or meaningful information. It often provides little value to users and search engines. Thin content can result from low-quality or short articles, pages with minimal text, or content that doesn’t address the user’s query effectively. Search engines may penalize or rank such content poorly in search results.
Keyword stuffing : Keyword stuffing is a black hat SEO technique where a webpage is loaded with an excessive number of keywords or phrases in an attempt to manipulate search engine rankings. This practice results in low-quality and unnatural content that doesn’t provide value to users. Search engines may penalize or devalue such pages.
Black hat SEO : Black hat SEO refers to unethical and prohibited techniques used to manipulate search engine rankings. These practices violate search engine guidelines and may include keyword stuffing, cloaking, link manipulation, and content scraping. Black hat methods can result in penalties, loss of search visibility, and harm to a website’s reputation.
White hat SEO : White hat SEO refers to ethical and approved techniques used to improve search engine rankings and enhance website visibility. These practices align with search engine guidelines and include high-quality content creation, keyword optimization, link building through natural means, and user-focused strategies. White hat SEO aims for long-term, sustainable results while maintaining website integrity.
Gray hat SEO : Gray hat SEO is a middle-ground approach between white hat and black hat SEO practices. It involves using tactics that are not explicitly prohibited by search engines but may push ethical boundaries. Examples include buying expired domains for backlinks or using clickbait headlines. Gray hat strategies can deliver short-term gains but may risk penalties and long-term reputation damage.
301 redirect : A 301 redirect is a permanent HTTP status code used in web development to automatically redirect one URL to another. It informs both users and search engines that a webpage or resource has been permanently moved to a different location. This helps maintain search engine rankings and ensures a seamless user experience during the transition.
404 error : A 404 error, also known as “Not Found,” is an HTTP status code indicating that the requested webpage or resource could not be located on the server. It typically occurs when a URL is mistyped, deleted, or no longer exists. A 404 error informs users that the page they are looking for cannot be found.
Canonicalization : Canonicalization is an SEO process used to manage duplicate content issues on websites. It involves specifying the preferred or canonical version of a webpage when multiple URLs have similar or identical content. Search engines then prioritize the canonical URL, consolidating ranking signals and avoiding duplicate content penalties.
HTTPS : HTTPS, or HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure, is a secure communication protocol used for data transmission on the internet. It encrypts the data exchanged between a user’s web browser and a website’s server, ensuring privacy and security. Websites with HTTPS display a padlock icon in the browser’s address bar, indicating a secure connection.
SSL certificate : An SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate is a digital certificate that establishes a secure, encrypted connection between a user’s web browser and a website’s server. It ensures the confidentiality and integrity of data transmitted, making it difficult for malicious actors to intercept or tamper with sensitive information.
Keyword density : Keyword density is a metric in SEO that measures the frequency of a specific keyword or phrase within a web page’s content, expressed as a percentage of the total word count. It helps assess keyword relevance but should be used in moderation to avoid keyword stuffing, which can harm SEO.
SERP features : SERP features, or Search Engine Results Page features, are elements and enhancements displayed alongside organic search results in search engine results pages (SERPs). Examples include featured snippets, knowledge panels, local packs, and video carousels. These features provide additional information and context to users, aiming to address their queries more comprehensively.
Crawling errors : Crawling errors in SEO refer to issues encountered by search engine bots or crawlers when they attempt to access and index web pages on a website. These errors can include 404 (Not Found) errors, server errors, or issues with robots.txt files, preventing search engines from properly indexing content. Fixing these errors is crucial for SEO.
SEO plugin (e.g., Yoast SEO) : An SEO plugin, such as Yoast SEO for WordPress, is a software extension that enhances a website’s SEO capabilities. It provides tools and features to optimize on-page elements like meta tags, content, and readability. SEO plugins offer suggestions and analysis to help improve a website’s search engine visibility and user-friendliness.
User-generated content (UGC) : User-generated content (UGC) is content, such as reviews, comments, photos, or videos, created and shared by a website’s users or customers. It can contribute to a website’s authenticity, engagement, and community building. UGC is often found in social media, online forums, and e-commerce sites, enhancing user experiences.
LSI keywords (Latent Semantic Indexing) : LSI keywords (Latent Semantic Indexing) are words or phrases related to a primary keyword or topic in a piece of content. Search engines use LSI keywords to understand the context and relevance of content. Including LSI keywords in content helps improve its search engine ranking and provides a more comprehensive user experience.
Crawling depth : Crawling depth, in SEO, refers to the level or extent to which search engine bots navigate and index a website’s pages. It indicates how deep within the site’s hierarchy the bots venture during the crawling process. Properly managing crawling depth ensures that important pages receive adequate attention from search engines.
SEO-friendly URL : An SEO-friendly URL is a web address that is designed to be easily understood by both users and search engines. It typically includes descriptive keywords related to the page’s content, uses hyphens to separate words, and avoids unnecessary characters or parameters. SEO-friendly URLs contribute to better search engine rankings and user experience.
Keyword cannibalization : Keyword cannibalization is an SEO issue where multiple pages on a website target the same or very similar keywords. This can confuse search engines and result in competing pages, diluting the site’s SEO efforts. Resolving keyword cannibalization involves optimizing content, consolidating pages, and improving keyword targeting strategy.
Nofollow attribute : The “nofollow” attribute is an HTML attribute used in hyperlinks to instruct search engines not to follow the linked URL and not to pass any SEO authority or ranking value to the linked page. It is often used for paid or untrusted links to prevent them from influencing search engine rankings.
Domain name : A domain name is a unique, human-readable web address used to identify and access websites on the internet. It serves as the website’s online identity and consists of a memorable name followed by a top-level domain (TLD), such as .com or .org. Domain names make it easier for users to locate and interact with websites.
Keyword competition : Keyword competition in SEO refers to the level of difficulty or competitiveness associated with ranking for a specific keyword or phrase in search engine results. It is influenced by the number of websites targeting the keyword and their relative authority. High competition keywords are harder to rank for, while low competition keywords are easier.
Inbound links : Inbound links, also known as backlinks, are hyperlinks from external websites that point to a specific webpage on another site. They play a significant role in SEO, influencing a site’s authority and search engine rankings. High-quality inbound links from reputable sources are valuable for improving a website’s online visibility and credibility.
Outbound links : Outbound links, also referred to as external links, are hyperlinks on a webpage that direct users to other websites or online resources outside the current website’s domain. Outbound links can provide additional information, references, or sources to users, contributing to a more comprehensive and informative web experience.
Natural links : Natural links, in the context of SEO, are backlinks that are acquired organically and without manipulation. They are typically earned when other websites voluntarily link to your content because they find it valuable and relevant. Natural links are highly regarded by search engines and contribute positively to a website’s authority and rankings.
Anchor text diversity : Anchor text diversity refers to the practice of using a variety of different anchor text phrases when creating backlinks to a website. Diverse anchor text includes a mix of keywords, branded terms, and generic phrases. This strategy helps improve the naturalness and SEO effectiveness of a link profile and avoids over-optimization.
SERP ranking : SERP ranking, or Search Engine Results Page ranking, refers to the position at which a webpage appears in search engine results for a specific keyword or query. Websites aim to achieve higher SERP rankings to increase their visibility and attract more organic traffic, as higher-ranked pages are typically more likely to be clicked on by users.
Blacklist : A blacklist is a list of items, such as websites, IP addresses, or email addresses, that have been identified as malicious, spammy, or harmful. It is used by various systems and organizations, including email servers and security software, to block or restrict access to or communication with items on the list, thus protecting users from potential threats.
SERP volatility : SERP volatility refers to the degree of fluctuation or instability in search engine results pages (SERPs) over time. High SERP volatility indicates frequent and significant changes in rankings for specific keywords or search queries, often due to algorithm updates, competition, or other factors. Low volatility suggests more stable and predictable rankings.
AdWords : AdWords, now known as Google Ads, is an online advertising platform developed by Google. It allows advertisers to create and manage pay-per-click (PPC) advertising campaigns. Advertisers bid on keywords to have their ads displayed in Google’s search results and on the Google Display Network. Advertisers pay when users click on their ads.
PPC campaign : A PPC (Pay-Per-Click) campaign is an online advertising strategy in which advertisers pay a fee each time their ad is clicked by a user. These campaigns are typically managed through platforms like Google Ads or Bing Ads and involve bidding on keywords to have ads displayed in search engine results or on websites. Advertisers set budgets and target specific demographics to optimize their campaign’s effectiveness.
Landing page optimization : Landing page optimization is the process of improving the design, content, and user experience of a webpage where visitors “land” after clicking on an online advertisement or a search engine result. The goal is to maximize conversions and achieve specific marketing objectives, such as lead generation or sales, through A/B testing, content refinement, and usability enhancements.
Conversion tracking : Conversion tracking is a digital marketing process that monitors and analyzes user actions on a website to measure specific goals or actions taken by visitors. It helps businesses understand the effectiveness of their online marketing efforts, such as ad campaigns or website optimizations, by tracking events like form submissions, purchases, or sign-ups.
Traffic analysis : Traffic analysis is the process of examining data related to website visitors and their interactions with a website. It involves collecting and analyzing metrics like page views, unique visitors, bounce rates, and referral sources to gain insights into user behavior. Traffic analysis helps businesses make informed decisions about website improvements and marketing strategies.
Google Analytics : Google Analytics is a web analytics service provided by Google. It allows website owners and marketers to track and analyze user behavior on their websites. Google Analytics provides valuable insights into website traffic, audience demographics, and user interactions, helping businesses make data-driven decisions to improve their online presence and performance.
Keyword ranking report : A keyword ranking report is a document that provides information about the positions of specific keywords or phrases in search engine results pages (SERPs). It tracks keyword rankings over time, helping website owners and marketers assess the effectiveness of their SEO efforts and identify areas for improvement in search engine visibility.
Content management system (CMS) : A Content Management System (CMS) is a software platform that allows users to create, edit, organize, and publish digital content, typically for websites. It simplifies content creation and management, providing tools for text, images, videos, and more. Popular CMSs include WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal, enabling users to update websites without advanced technical knowledge.
Blogging : Blogging is the practice of regularly creating and publishing written, multimedia, or visual content on a blog. Bloggers share information, opinions, or stories on various topics, often in a chronological format. Blogging serves purposes such as personal expression, knowledge sharing, and marketing, helping individuals and businesses engage with online audiences.
Social signals : Social signals refer to the collective engagement and interactions a piece of content receives on social media platforms. This includes metrics like likes, shares, comments, and retweets. Social signals are considered by search engines as indicators of content quality and relevance, potentially influencing search rankings and visibility.
User-generated signals : User-generated signals are data and interactions generated by website users. These signals can include comments, reviews, ratings, social media shares, and other forms of user-generated content. Search engines and online platforms often use these signals to evaluate the quality and trustworthiness of a website or online resource.
XML sitemap : An XML sitemap is a structured file that lists all the web pages and content on a website, designed to help search engines index and crawl the site more effectively. It provides metadata about each page, such as its URL and last modification date, making it easier for search engines to understand a website’s structure and prioritize content for indexing.
Above the fold : “Above the fold” refers to the portion of a web page that is immediately visible to users without scrolling down. It is the area of the page that appears on a user’s screen when they first land on a website. Content placed here is considered more prominent and likely to capture user attention.
Below the fold : “Below the fold” refers to the content on a web page that is not immediately visible when a user first arrives on the page and must scroll down to see. This content is located beneath the initial visible portion and may require user interaction to access.
Search engine crawler : A search engine crawler, also known as a web crawler or spider, is a computer program that systematically and automatically navigates the internet to discover, index, and gather information from web pages. Search engine crawlers are used by search engines to update their databases and provide search results to users.
SERP snippet : A SERP snippet, or Search Engine Results Page snippet, is a brief preview of a web page’s content displayed in search engine results. It typically includes the page’s title, URL, and a meta description. Snippets provide users with a glimpse of what a page is about and help them decide which result to click on.
Keyword density : Keyword density is a measure of how frequently a specific keyword or phrase appears in a piece of content, expressed as a percentage of the total word count. It is used in SEO to assess keyword relevance, but excessive keyword density (keyword stuffing) can negatively impact rankings and user experience.
Keyword prominence : Keyword prominence in SEO refers to the placement and visibility of a specific keyword within a webpage’s content. It indicates how prominently or prominently the keyword is featured, typically focusing on its position in headings, titles, and the first paragraphs of content. Proper keyword prominence can enhance a page’s relevance for search engines.
Keyword proximity : Keyword proximity is an SEO term that describes how closely related two or more keywords are within a piece of content. It measures the distance between keywords in a sentence or phrase. The closer the keywords are, the higher their proximity, which can indicate a stronger semantic relationship and improve content’s search engine ranking.
Keyword research tools (e.g., SEMrush, Ahrefs) : Keyword research tools like SEMrush and Ahrefs are software platforms designed to help SEO professionals and website owners discover relevant keywords for their content. They provide data on search volume, keyword competition, and related phrases, aiding in the selection of high-performing keywords to target in content optimization and search engine marketing efforts.
Keyword planner : A keyword planner is a tool provided by search engines, such as Google Keyword Planner, that assists advertisers and SEO professionals in identifying and analyzing keywords relevant to their campaigns. It offers insights into search volume, competition, and keyword suggestions, helping users make informed decisions when targeting specific keywords for advertising or content optimization.
Query : A query is a specific request or question entered by a user into a search engine or database seeking information or results. In the context of search engines, it typically consists of keywords or phrases, and the search engine returns relevant web pages, documents, or information based on the query’s intent and content.
Organic traffic : Organic traffic refers to the visitors who arrive at a website through unpaid, natural, and non-advertising channels, primarily through search engine results. It includes users who find a website by entering relevant keywords in a search engine and clicking on the organic (non-paid) search results. Organic traffic is a crucial metric in SEO and indicates a website’s visibility and relevance in search engines.
Paid traffic : Paid traffic refers to website visitors who arrive through paid advertising efforts, such as pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns, display ads, or sponsored content. It involves advertisers paying for each click or impression to drive users to their websites. Paid traffic is a component of online marketing and can be targeted to specific demographics and keywords.
Domain Expiration: This refers to the date when a registered domain name ceases to be active. If not renewed, the domain becomes available for purchase by others, leading to potential website downtime and loss of online identity.
URL Structure: It encompasses the way web page addresses are organized, aiding user navigation and search engine indexing. A well-structured URL is user-friendly, often reflecting the content’s hierarchy and improving SEO.
Canonical Domain: The preferred version of a domain used to avoid duplicate content issues. Canonicalization helps search engines understand the authoritative source of content to prevent indexing conflicts.
Subdomain: A subset of a domain, indicated by a prefix in the URL, used to host distinct content or functions while remaining under the primary domain’s umbrella.
Internal Link Juice: This signifies the flow of SEO value or authority within a website through internal linking, reinforcing the relevance and hierarchy of pages.
External Link Juice: It represents the transfer of SEO authority from external websites through backlinks, potentially enhancing your site’s search engine rankings.
Natural Link Profile: A backlink profile consisting of high-quality, contextually relevant links, acquired through ethical methods, contributing positively to SEO.
Reciprocal Link: An agreement between websites to link to each other, which, when overused, can be considered a spammy practice by search engines.
Keyword Cannibalization: Occurs when multiple pages on a website compete for the same keyword, causing confusion for search engines and potentially resulting in lower rankings.
Link Bait: High-quality website content designed to attract backlinks organically due to its exceptional value and relevance, bolstering SEO efforts.
Outbound Link: A hyperlink from your site to an external webpage, often used to provide additional resources for users while potentially influencing SEO.
Inbound Link: Commonly known as a backlink, it is a hyperlink from an external website to yours, capable of enhancing your site’s authority and search engine rankings.
Content Scraping: The unethical practice of copying content from one website and publishing it on another without proper attribution or permission, potentially resulting in copyright violations.
Black Hat SEO Tactics: Unethical and manipulative strategies that violate search engine guidelines, risking penalties and compromising website integrity.
Doorway Page: A webpage designed solely for search engines, typically featuring thin content and redirects to the main site, aimed at manipulating search engine rankings.
Cloaking: A deceptive practice where the content shown to search engines differs from what users see, violating search engine guidelines and integrity.
Grey Hat SEO Tactics: Strategies that fall between ethical (white hat) and unethical (black hat) practices, often considered risky due to their potential for penalties.
Negative SEO: Deliberate actions by competitors or malicious entities to harm a website’s rankings through manipulative tactics, spammy links, or other unethical means.
User Engagement: The degree of interaction and involvement that users exhibit when interacting with a website, encompassing metrics such as time spent on site, page views, comments, and social sharing. High user engagement is indicative of a positive user experience.
CTR Optimization: The process of improving Click-Through Rate (CTR) through strategies like compelling titles and meta descriptions, aiming to increase the number of users clicking on a search result or ad.
Conversion Optimization: The practice of enhancing a website or landing page to maximize the likelihood of visitors taking a desired action, such as making a purchase or filling out a form.
A/B Testing: A method of comparing two versions of a webpage or an element to determine which one performs better in terms of achieving specific goals, helping refine website optimization strategies.
Heatmap: A graphical representation of user interactions on a webpage, typically showing where users click or spend the most time. Heatmaps assist in identifying areas of user interest and potential issues.
Exit Rate: A metric indicating the percentage of visitors who leave a website from a specific page, which can provide insights into the effectiveness of that page’s content or design.
Google Search Console: A web service by Google that allows website owners to monitor their site’s performance in Google Search, offering insights into indexing, search queries, and potential issues.
Bing Webmaster Tools: A similar tool to Google Search Console but designed for Bing search engine, providing webmasters with data and insights about their site’s performance on Bing.
Keyword Stuffing: An outdated and spammy SEO practice involving excessive use of keywords on a webpage to manipulate search engine rankings, which can result in penalties.
Keyword Spamming: A similar practice to keyword stuffing, involving the excessive and irrelevant use of keywords to manipulate search results, violating search engine guidelines.
Keyword Research Intent: The process of understanding user search intent behind specific keywords to create content that aligns with the users’ informational, navigational, or transactional needs.
Query Intent: The purpose or goal behind a user’s search query, often categorized as informational (seeking information), navigational (finding a specific website), or transactional (looking to make a purchase or take an action).
Ad Placement: The strategic positioning of advertisements within a webpage or online platform to maximize visibility and engagement with target audiences.
Ad Position: The specific rank or placement of an advertisement on a search engine results page or website, which can impact its visibility and click-through rate.
Quality Backlinks: High-quality and authoritative inbound links from reputable websites, which can significantly boost a site’s SEO and credibility.
Trust Signals: Indicators, such as positive reviews, testimonials, and trust badges, that instill confidence in users and search engines, enhancing a website’s credibility.
Link Profile: The collection of all inbound and outbound links associated with a website, which search engines analyze to assess a site’s authority and relevance.
Google Knowledge Graph: A knowledge base used by Google to enhance search results by providing information about entities (people, places, things) and their relationships.
Long-Form Content: Comprehensive and in-depth content that covers a topic extensively, often providing value to readers and improving SEO due to its depth.
Short-Form Content: Brief and concise content, suitable for quick consumption, often used for topics that do not require extensive elaboration.
Recency Factor: The consideration of how recent content is when determining its relevance in search results, particularly important for topics with time-sensitive information.
Google Panda: An algorithm update by Google aimed at improving the quality of search results by penalizing websites with low-quality or duplicate content.
Google Penguin: An algorithm update focused on penalizing websites that engage in manipulative link-building practices and spammy techniques.
Google Hummingbird: An algorithm update designed to better understand user search intent and deliver more contextually relevant search results.
Google RankBrain: A machine learning component of Google’s algorithm that aids in understanding and ranking search results based on user intent.
User-Generated Signals: Data generated by user interactions on a website, such as comments, reviews, and social media contributions, which can influence SEO and user trust.
Social Media Signals: Indicators of a website’s popularity and authority based on its presence and interactions on social media platforms, impacting search engine rankings.
User Experience (UX) Signals: Factors that assess how well a website caters to users’ needs and expectations, including page speed, mobile-friendliness, and overall usability.
Google Ads: Google’s advertising platform, allowing businesses to create and display ads on the Google search network and other partner sites.
Display Network: A network of websites and platforms where Google Ads can display ads, including banner ads, to reach a broader audience.
Search Network: Part of Google Ads where advertisers bid on keywords to display text ads on search engine results pages (SERPs) when users search for those keywords.
Responsive Ads: Advertisements designed to adapt to various screen sizes and devices, ensuring a consistent and effective user experience.
Conversion Funnel: The stages that a user goes through from initial awareness to taking a desired action, such as making a purchase, often represented as a funnel shape.
Keyword Mapping: The process of assigning specific keywords to relevant pages on a website, ensuring that each page is optimized for a specific set of keywords, enhancing SEO and user experience.

